Technological Applications of Shape Memory Materials
The use of shape memory materials (SMMs) in technological applications is based on leveraging some of their particular behaviors (or a combination of them) associated with the existence of a reversible martensitic transformation. SMMs can develop recoverable forces or deformations or dissipate mechanical energy, achieving high efficiency indices in relation to their volume or weight when compared to other devices (servomotors, electromagnetic, etc.). SMMs with biocompatible properties, such as the NiTi-based alloy family, are of great interest in the medical industry.
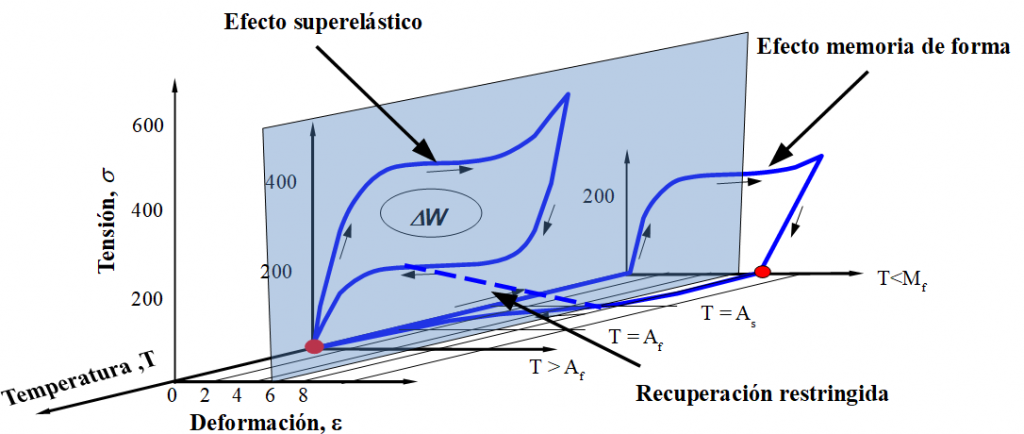
Research related to this line of investigation begins with the experimental characterization of different SMMs and thermo-mechanical treatments to optimize their different behaviors. An important aspect lies in their stability under cyclic repetition (functional properties - functional fatigue). Experimental techniques include conducting mechanical tests at controlled temperatures, resistivity tests, and differential calorimetry. Complementary to this, models of SMMs are developed to advance the understanding of the different mechanisms involved in their behaviors.
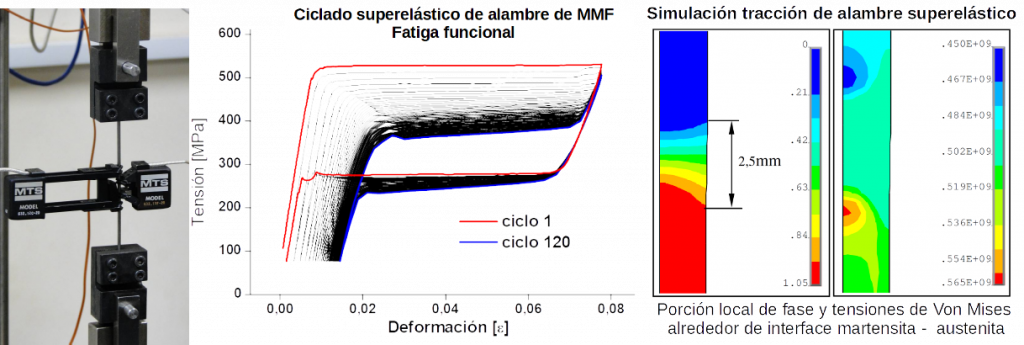
Simultaneously, a significant portion of the activities are aimed at developing experimental facilities for the various proposed applications, which involves combining knowledge acquired in SMMs with tasks of design, manufacturing, and prototype testing. In this case, behavior models are also developed to evaluate the performance of the designed systems.
The different technological applications of SMMs developed in the Division can be grouped according to the following classification. (Following the links, specific information for each one can be found)
1. SMMs used as linear actuators:
1.1 Actuation systems for mechanical testing machines
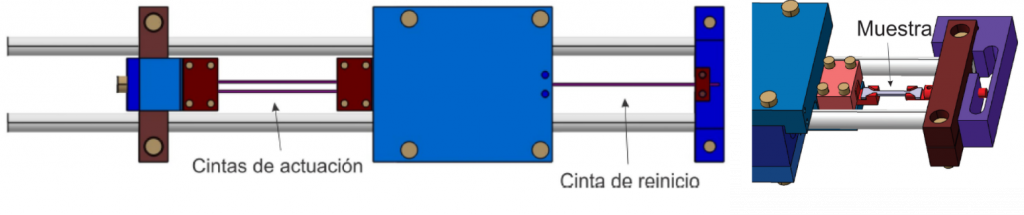
1.2 Manipulator systems actuated by SMM tapes
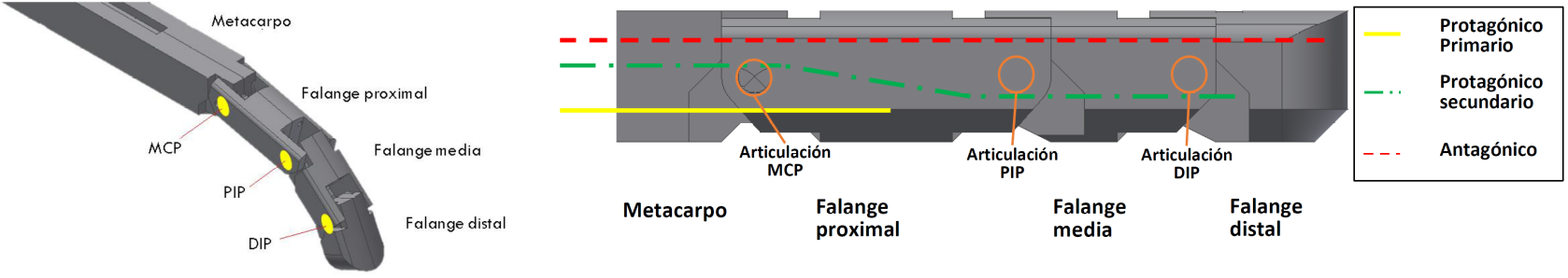
2. SMMs used as energy dissipators
2.1 Protection systems for anti-seismic structures

3. SMMs used as force actuators
3.1 Release devices for the aerospace industry
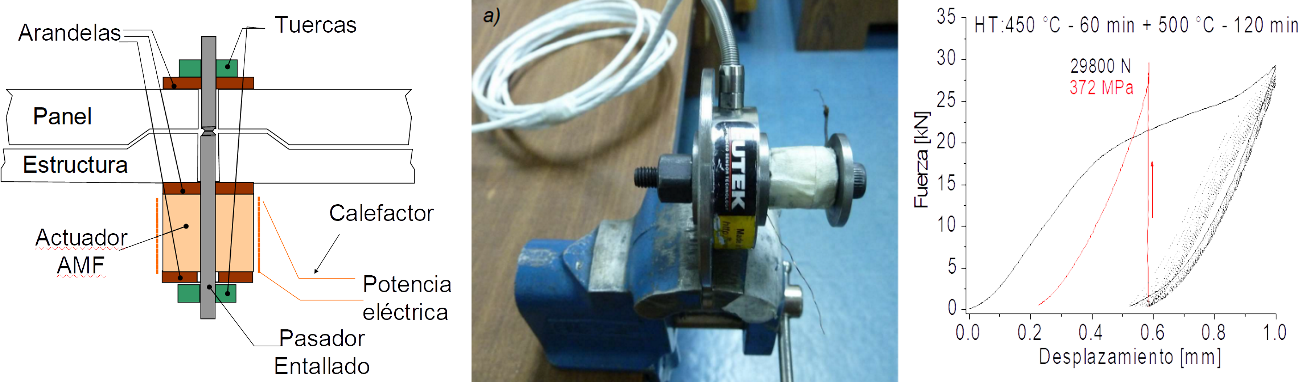
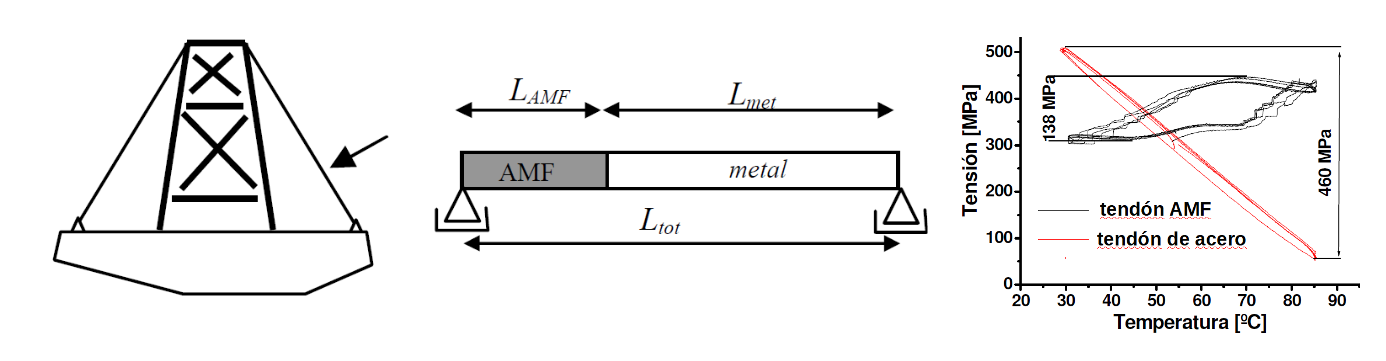
3.2 Thermal stress compensation systems for tendon-stabilized structures
Related publications Associated techniques and equipment Work on the topic!
